Infra: A Promising Way To Manage Kubernetes Users

Managing Kubernetes can be complex, and finding tools to simplify its use is crucial. Infra deserves some attention on how it can help manage cluster access.
Kubernetes is not a secure platform. Its implementation in production requires the integration of several components to ensure its security and good operation by both administrators and users.
The management of cluster access is obviously an important point in the adoption of the platform. Several tools exist today to manage this critical security aspect. Infra is a new player in this field and deserves some attention.
What Is Infra?
Infra is an open-source tool developed by InfraHQ to facilitate access management to different platforms, starting with Kubernetes. The product is still in development at the time of writing this article, but it already has some interesting features (described in the next sections) to facilitate the adoption and use of Kubernetes.
Infra integrates with existing or new clusters thanks to its simple architecture, consisting mainly of five modules:
- Infra Server, the heart of the system and the single point of entry for all connection and configuration requests
- Infra Database, to store configuration and useful information such as connection history
- Infra Connector, the agent to be deployed on all Kubernetes clusters in order to manage access to them from the central server
- Infra CLI (Command Line Interface), which allows interaction with the server, used by both administrators and users of the service
- Infra Providers, a source of truth for the list of users and groups to use to attach permissions to
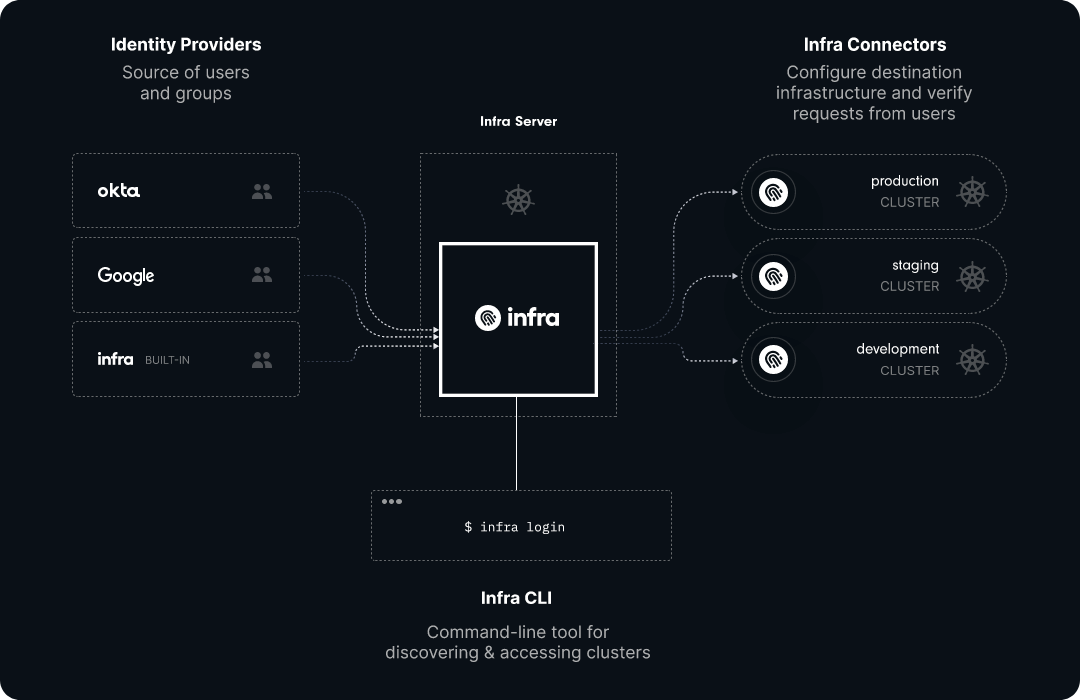
Infra’s architecture and its integration with various identity providers make it a good candidate to centralize user management in a unique source of truth. It allows administrators to decouple user management from the enterprise infrastructure. For example, multi-cloud or on-premises companies can focus their efforts on an identity provider like Google or Okta instead of relying on multiple LDAP servers or multiple Identity Access Management (IAM) services.
How to Deploy Infra
Infra tries to follow the good development and application management practices deployed on Kubernetes. Its installation is based on a Helm chart to easily customize the installation according to the context.
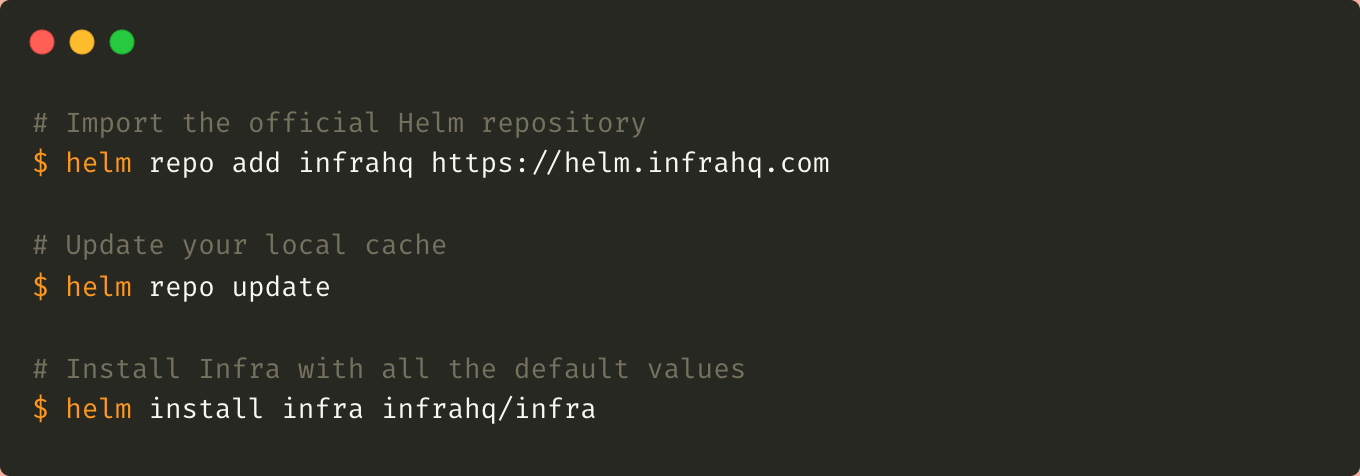
The customizable definition file can be found on GitHub. This application can be the only entry point for all Kubernetes users. It is recommended to enable or update some configuration options to make it production-ready, such as:
- Create an ingress rule to give a unique name to the Infra server and facilitate the adoption by the end users
- Disable the LoadBalancer service to rely on the Ingress controller
- Allow the metric collector and Prometheus rules to track useful information and get failure alerts
- Update resources (CPU and memory) according to estimated load
- Update the storage class name according to your context to store the Infra database and potentially back up the volume
- Enable automatic scaling of pods to ensure service is operational even on heavy load
When to Use Infra
With its architecture, Infra can easily integrate with any Kubernetes cluster, on-premise or cloud-based, existing or new one. Its ease of use and configuration makes this tool a good candidate for different uses.
Access Centralization
Centralizing access management to different Kubernetes clusters is a good practice to facilitate the administration of resources, especially during the onboarding and offboarding phases by relying on an external identity service itself centralized and potentially fully automated like Okta.
This practice minimizes the effort required to manage Kubernetes users by relying on a highly available cloud authentication service and thus, avoid the internal management of an LDAP service.
Granular Access Management
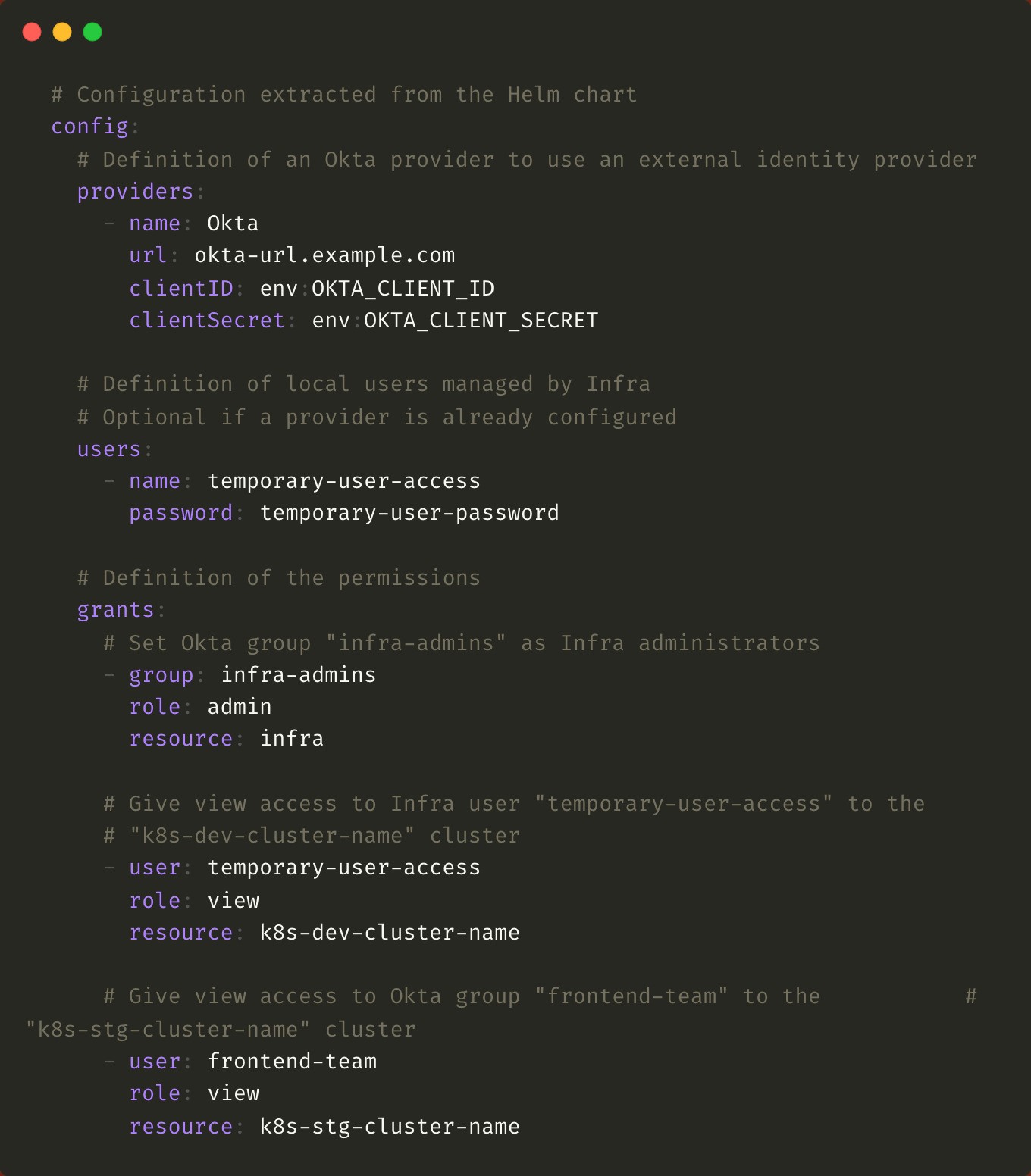
Infra has a granular access management system based on simple principles:
- A user or a group defining the user identity
- A role (specific to Infra) defining a permission group, three levels of permissions come by default: admin, read, write
- A scope of action defining the resources to which to apply permissions. The scope can currently be restricted to two levels: an entire cluster or a specific namespace
This granularity of access management is convenient because it makes it easy to manage global access, such as:
- All developers can access in read only a set of namespace (read-only role)
- The entire DevOps team has access to the administration of all the clusters (admin role)
- The frontend team can manage the Kubernetes resources deployed in their namespaces in the development environment but can only read in other environments like production
This granular management coupled with an external identity service makes Infra an ideal candidate to facilitate access and therefore the adoption of Kubernetes by all users.
Improve the Auditability of Kubernetes
Any platform deployed in production must be auditable to control the use of the platform. Kubernetes requires a number of tools to ensure a minimum level of security for containerized applications. Their accessibility is an important point in the platform’s auditability. It is essential to control access to clusters, Kubernetes APIs, managed resources, logs, and so on.
Infra allows you to control this by forcing all users to use its command line (CLI) to authenticate to a Kubernetes context to view resources. The creation of config files (kubeconfig for example) is no longer necessary and even deprecated in order to keep access control.
This process facilitates accessibility while facilitating the auditability of the platform by keeping all authorized and unauthorized access requests in the logs. A feature is announced at the time of writing to facilitate the reading of these data from the user interface of Infra.
How Easy Is It to Manage Access?
The management of access to a platform such as Kubernetes is unique to each company. Even if standards exist today, this management is strongly linked to a company’s security policy and therefore its level of auditability.
From the point of view of a site reliability engineer (SRE), it is important to simplify access to this type of platform while ensuring its security. The simplicity of an application is based on several points:
- Its integration with external services potentially already used by the company as an external identity service (Google, for example) that would allow using existing user groups to provide access to Kubernetes resources
- Its automation because this point is now crucial for all companies to guarantee the efficiency and reproducibility of the configurations
- Its supervision to ensure its operability at all times
- Its maintainability and documentation facilitate the understanding and evolution of the platform
- Its auditability to ensure compliance with the security policy in place
- Its ease of use ensures adoption of the platform
Infra is well on its way to checking all these boxes, and can therefore become a major player in Kubernetes user management thanks to its architecture, which is based on three components:
- Providers to use an external identity platform such as Okta, Google, and so on
- Users to use Infra as an identity provider or to define temporary accesses. This definition is not required if a provider is already configured.
- Grants to attach permissions to a group or user
Outsourcing the management of Kubernetes accesses by grouping them in a cloud service is a good practice to simplify the onboarding and offboarding processes while ensuring a level of security necessary for the use of the platform in production.
How Easy Is It to Get Access?
From a developer’s point of view, Infra has a big advantage because it greatly simplifies access to different resources and brings a certain abstraction of Kubernetes architecture.
Indeed, no need to manage or understand the notion of kubeconfig file, or Kubernetes context. Infra handles this for the user autonomously. With each login, the Infra command line will automatically configure all the contexts to which the user has access to allow him to swipe quickly between them. This automation allows a user to use any Kubernetes client (Kubectl, Lens, Scaffold, and so on) naturally without having to configure anything. This ease of access promotes the adoption of the platform and therefore its use.
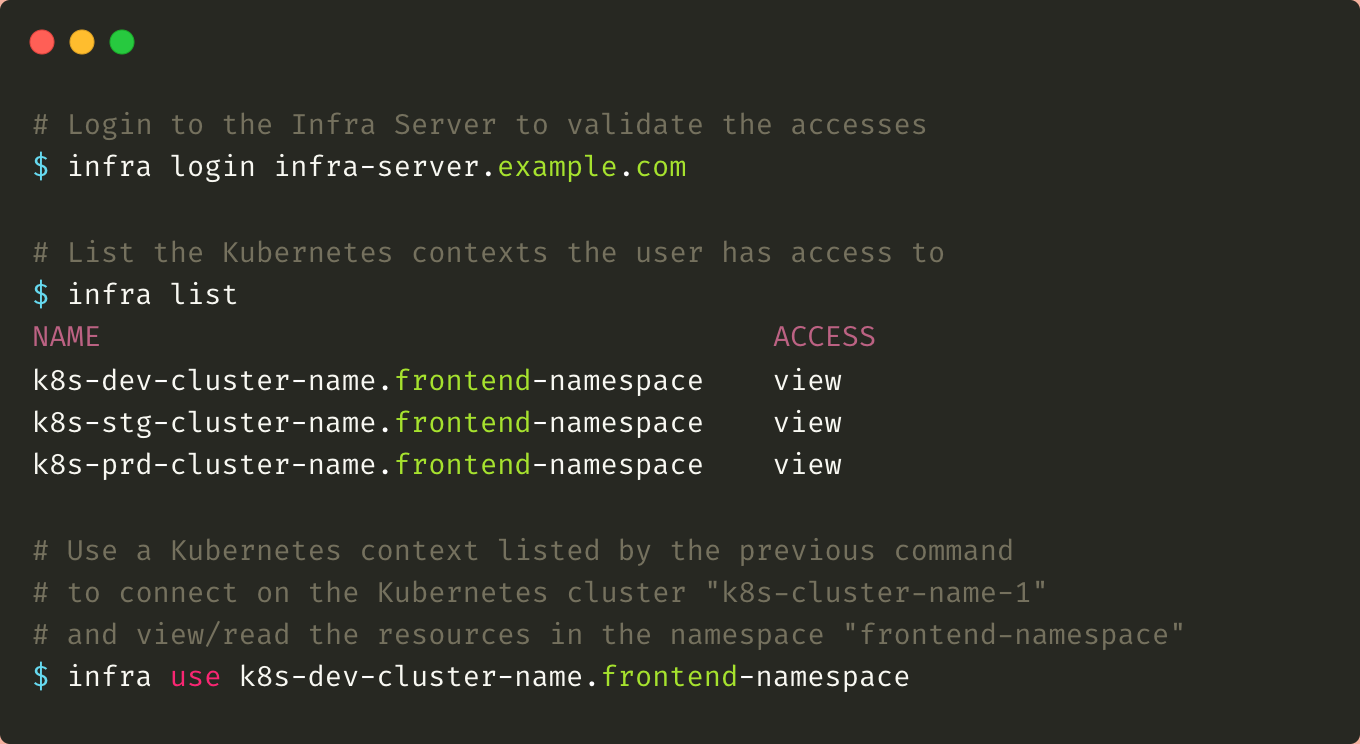
A developer should use three daily commands:
- Infra login to connect to the server and validate these accesses
- Infra list to list the resources (clusters or namespaces) to which it has access
- Infra use to enable a specific Kubernetes context. This command is optional because it depends on the client used.
Kubernetes is a complex platform. Simplifying its access and use is certainly the best approach.
We Provide consulting, implementation, and management services on DevOps, DevSecOps, Cloud, Automated Ops, Microservices, Infrastructure, and Security
Services offered by us: https://www.zippyops.com/services
Our Products: https://www.zippyops.com/products
Our Solutions: https://www.zippyops.com/solutions
For Demo, videos check out YouTube Playlist: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=4FYvPooN_Tg&list=PLCJ3JpanNyCfXlHahZhYgJH9-rV6ouPro
If this seems interesting, please email us at [email protected] for a call.
Relevant blogs
The 10 Commandments for Designing a Data Science Project
7 Top Open-Source Datasets to Train Natural Language Processing (NLP) and Text Models
How RPA Is Changing the Way People Work
The Database CI/CD Best Practice With GitHub
Recent Comments
No comments
Leave a Comment
We will be happy to hear what you think about this post