Zero Trust Security Model to Safeguard Software Apps
In this blog, we’ll look at how zero trust security can assist in delivering business value by allowing users to access their apps in a smooth and safe manner.
We've all heard a lot about digital transformation and how it affects the IT world. Each of these technologies, whether it's big data, the Internet of Things (IoT), or cloud computing, has made a significant contribution to a range of enterprises. Few people, however, talk about the complexity they add, especially in the context of business network infrastructures.
The fences are crumbling, and there is a hazy peripheral that is causing security concerns.
To be exact, the adoption of mobile internet, cloud computing, and other technologies are permitting outside platforms to penetrate the enterprise, while the open and supportive needs of emerging technologies, such as IoT and big data, are enabling external platforms to reach the enterprise.
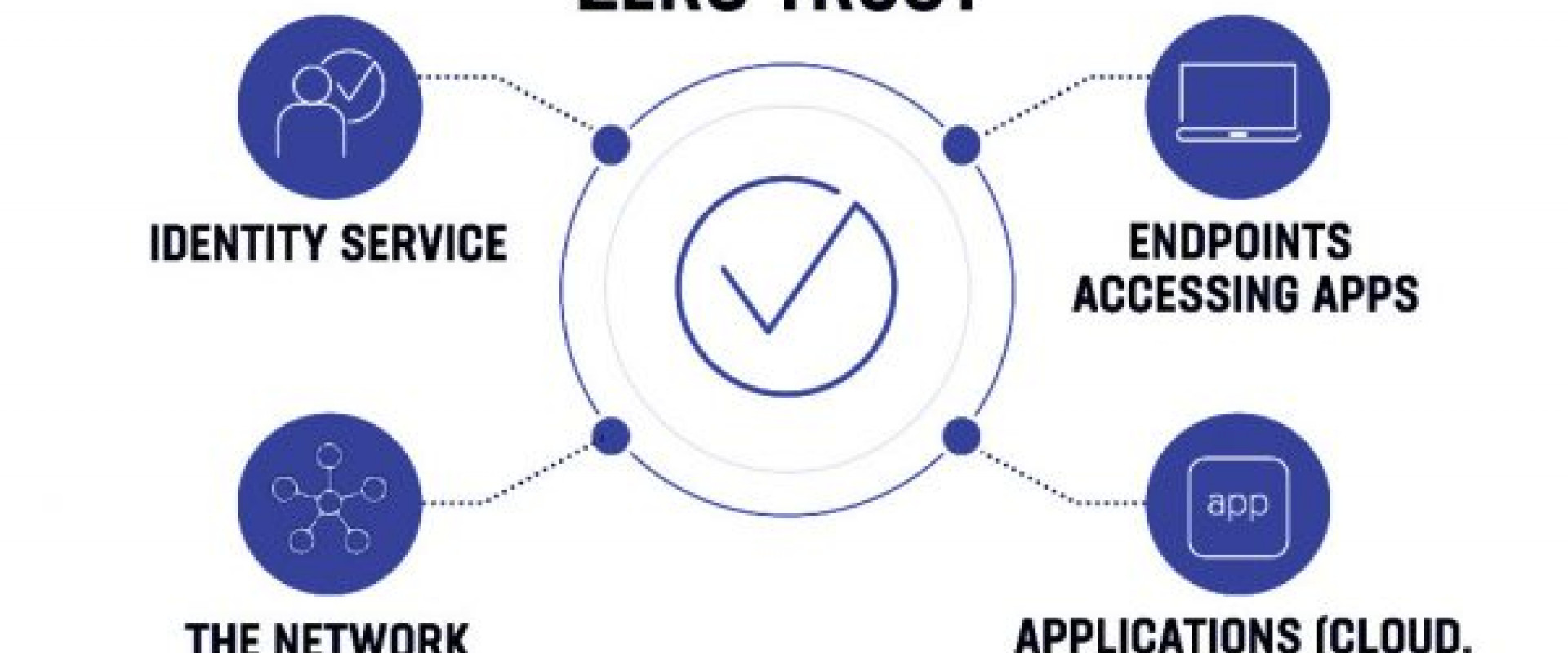
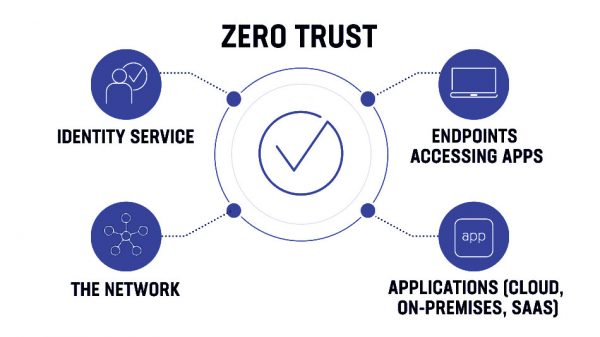
A zero trust architecture (ZTA) is a security approach based on the idea that every user and device within and outside of an organization’s boundaries must be validated before access is granted. In this blog, we’ll look at how zero trust security can assist in delivering business value by allowing users to access their apps in a smooth and safe manner.
Introduction to Zero Trust Model
Zero Trust is a network security architecture based on tight identity verification. Only validated and authorized users and devices are allowed to access apps and data, according to the framework. Simultaneously, it protects such apps and users from sophisticated internet dangers.
Although not a fully new idea, this model was initially developed by a Forrester Research analyst. With time it has become more relevant for today’s digital transformation and its influence on enterprise network security architecture.
Groundwork to Zero Trust Model
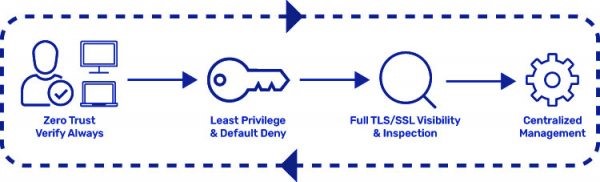
We see Zero Trust as a well-thought-out concept that can be used to build a cybersecurity ecosystem. As a result, this informs a lot about what we want to achieve as a final aim after implementing this approach.
The three pillars of the zero-trust security model are:
Remove all Connections
Many systems, like firewalls, employ a transit strategy, in which data are transferred to their receivers while being reviewed. Under this, a notice is given if a malicious file is found, but it is typically too late. The usefulness of Zero trust is that it closes all connections to allow it to keep and analyze unfamiliar files before they reach the destination. There is a proxy architecture that takes charge of inspecting all communication at line speed; this includes encrypted traffic, further supported by deep data and threat analysis.
Eliminate Attack Surface to Reduce Risk Frequency
Because of zero trust, users are only connected to the apps and services they require and are never linked to networks. Allowing one-to-one connections, reduces the likelihood of lateral movement and prevents a compromised device from targeting other network resources. It’s worth noting that people and apps with zero trust are invisible to the internet and hence cannot be tracked or targeted.
Data Protection Using Granular Policies
Zero trust uses the user identification and device posture to intelligently verify access privileges. It’s also recognized for employing specific business regulations based on contexts, such as device, user, requested app, and content kind. The user’s access capabilities are regularly examined when the context changes, such as the user’s device or location, since the policies are adaptable.
Advantages of Zero Trust for Businesses
Good Control Over Cloud and Container Environments
When it comes to moving to and using the cloud, security experts are most concerned about the loss of visibility and access management. Despite notable advances in cloud service provider (CSP) security, the idea of workload security remains a joint responsibility of the CSP and the cloud-using company.
When a zero-trust architecture is implemented, security policies are based on the identification of communicative workloads and are directly tied to the workload. As a consequence, security is kept as close as possible to the assets that need to be secured and is unaffected by network structures such as IP addresses and protocols. As a result, protection not only adapts to the workload in which it tries to communicate but also remains consistent as the environment changes.
Reduced Cases of Data Breach
Because zero trust is based on the principle of least privilege, each entity (device, user, and workload) is assumed to be hostile. Every request is reviewed, individuals and devices are confirmed, and permissions are assessed before confidence is created. Furthermore, every time the context changes, such as the user’s location or the data being accessed, this “trust” is continually reviewed.
As a result of being untrustworthy, an attacker who obtains access to the network or cloud instance through a compromised device or other weakness will be unable to take data. Furthermore, due to the zero-trust security approach of establishing a secure segment of one, there is no way to migrate laterally. As a result, the attacker will have nowhere to go and access will be blocked.
Facilitates in Compliance Initiatives
All user and company relationships are protected from being disclosed on the internet with zero trust. It is easier to prove compliance with privacy principles and other requirements due to its obscurity.
Additionally, zero trust segmentation may be used to create perimeters around specific categories of sensitive data. This includes data backups, PCI data, and credit card data. The adoption of fine-grained limits aids in the preservation of a clear data separation between regulated and non-regulated information. When it comes to flat network designs that provide over-privileged access in the event of a data breach, a zero-trust segmentation solution provides greater visibility and control.
Lesser Business and Organization Level Risks
All apps and services are harmful, according to zero trust, and they can’t communicate unless their identification traits can be positively authenticated.
As a result, zero trust reduces risk by exposing everything on the network, as well as how those assets connect. Since baselines have been established, it also reduces risk by deleting over-provisioned software and services and by regularly validating the credentials of each and every communication asset.
Conclusion
Businesses must maintain a zero-trust network architecture in order to remain competitive. It must be able to safeguard corporate data regardless of where users and devices are located, while also guaranteeing that applications run fast and smoothly.
To achieve a zero-trust architecture, it is advisable to contact a well-known security testing service partner that can assist you in keeping your application safe, adaptive, and scalable. Receiving industry-best security testing techniques is always a better plan for minimizing application risk at the earliest.
Recent Comments
No comments
Leave a Comment
We will be happy to hear what you think about this post